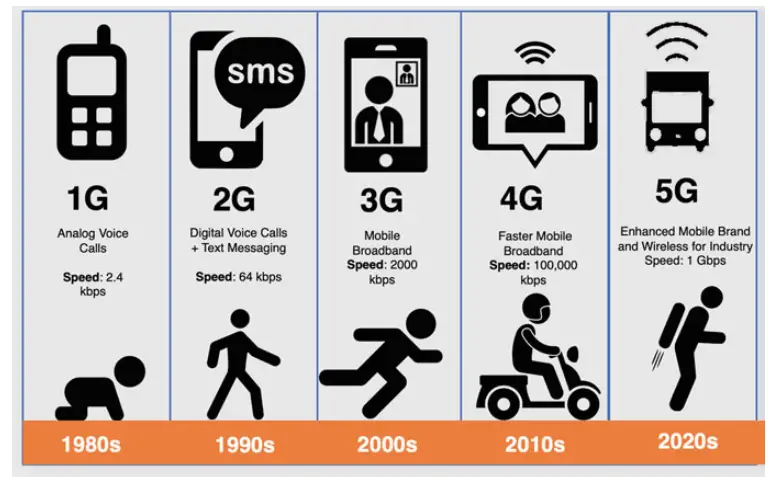
The journey from 1G to 5G
We have witnessed immense growth in telecommunication technology with unprecedented broadband enhanced via GPRS and data communication. It is expected that we will witness the use of 6G within 2030 , yes in just 6 years. The first generation (1G) of cellular network technology was introduced in the 1980s. It was prone to a certain limit due to analogue technology and limited capacity leading to poor performance. Digital technology was introduced through 2G offering text messages and voice calls. 3G gave us wireless capabilities with stone broadband and a speed of 2000 kbps. The introduction of 4G enhanced the same with mobile broadband with a speed of a whopping 100,000 kbps. The fifth generation (5G) focuses on improved wireless connectivity, ultra-fast download and upload speed and a better approach to multimedia streaming for increased experiences. The current speed of 5G is 1 Gbps, so is this the current limit, of course not, but what is the potential of 6G ? This article offers a journey Towards 6G networks: Use Cases and Technologies.
Check our news articles on current smartphone leaks by clicking on the respective links:
Key use cases of 6G Networks
Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB)
 Source: Hinrich Foundation
Source: Hinrich Foundation The major feature of the 6G is a stronger mobile broadband with ultra-high-speed internet. The collective development in the field of telecommunication and machine learning will offer 3D holographic communications. This will be supported through advanced Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR).
Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communications (URLLC)

High-speed internet connectivity 100 times faster than 5G will give us access to low-latency communication with real-time remote controls. The presence of real-time communication among autonomous vehicles, different control systems and drones will revolutionize the current transportation system across the globe.
Global Coverage and Connectivity

The increased telecommunication capacity will facilitate the promotion of satellite connectivity in remote and rural areas in the era of 6G. Global communication will become seamless and light-speed data transfer. This will be supported through untapped radio frequencies and cognitive technologies in 6G Networks.
Massive Machine Type Communications (mMTC)
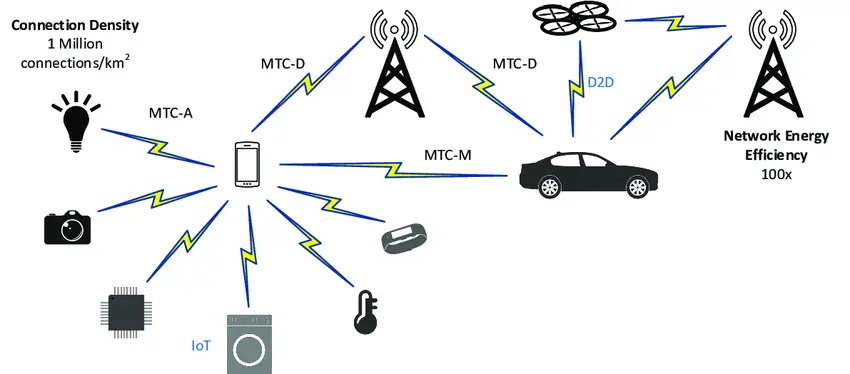
Development of smart cities with automated healthcare monitoring systems and advanced infrastructures. Introduction to 6G will guide the path towards efficient traffic management, resource optimization and automotive waste management. Other changes include increased Internet of Things (IoT) with billions of connected devices.
Key Technologies Enabling 6G
Quantum Communication

Advancement in the 6G will offer the application of Quantum technologies with its cryptographies and secured data transmission. This will strengthen the concept of cybersecurity making it hard for third parties to access and hack sensitive information. A significant amount of positive impact is expected on data protection activities with ultra-secure communication channels.
Edge and Fog Computing
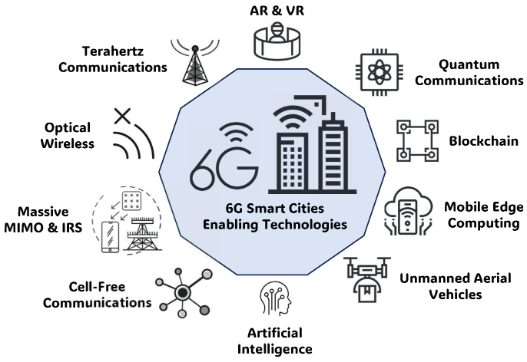
Edge and Fog Computing will substantially improve latency reduction and offer real-time responsiveness in data processing making it feel generative. The upcoming advancements in the telecommunication network will promote synergies with cloud computing and distributed computing.
Terahertz Communication
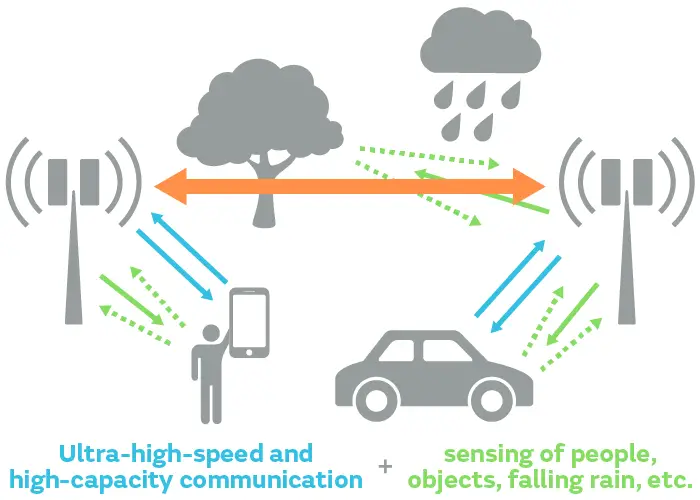
6G connectivity will increase a wide range of frequency bands stronger than millimeter waves with high capacities. The use of terahertz and sub-terahertz bands will complement the lower frequency spectrum alongside high data waves and efficient spectrum utilization.
Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RIS)
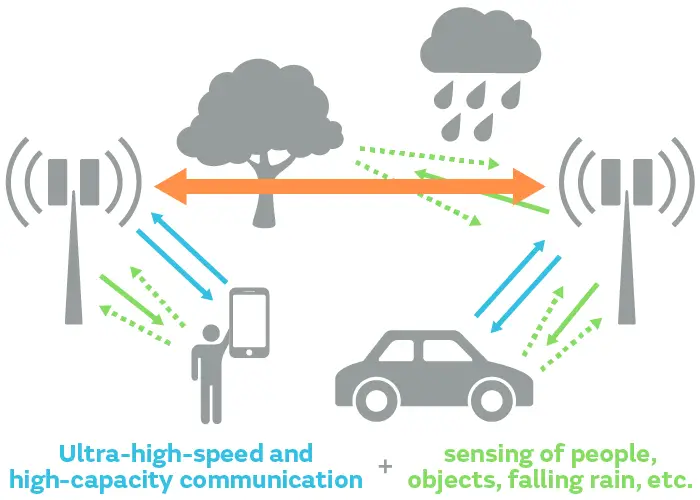
RIS for the upcoming networks will offer modern millimeter wave-enhancing wireless communication. Increases in sustainability and energy efficiency are another area of dynamic adaption that will enhance the data transmission process and strengthen data protection.
Potential Challenges Towards 6G Networks: Use Cases and Technologies
The potential challenges in brief include a lack of infrastructural developments and regulatory compliances. Possible concerns include hardware requirements, sustainable energy sources and spectrum availability. Furthermore, negative environmental impact due to wavelengths may hinder the establishment of upcoming 6G telecommunication.